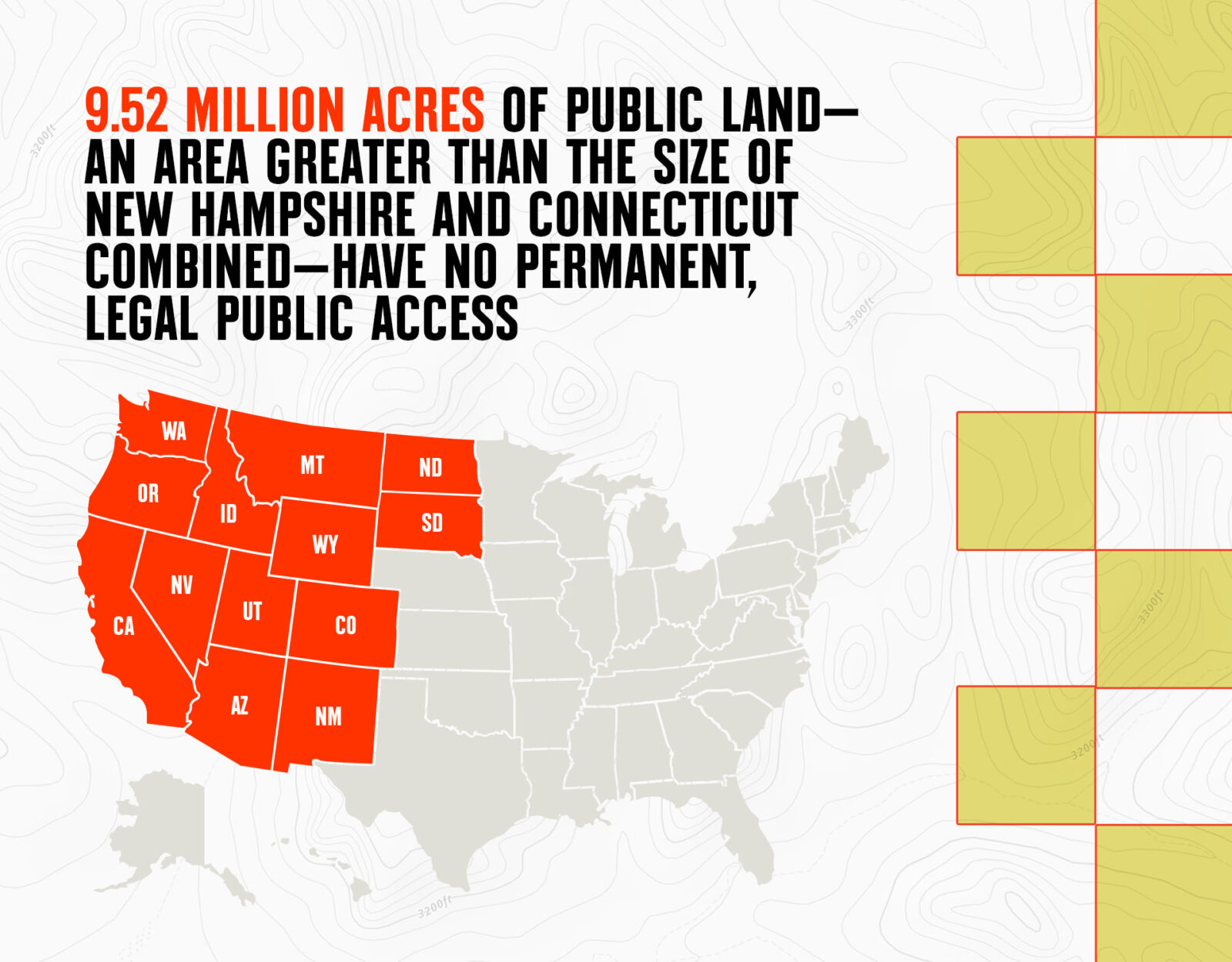
Have you ever wondered what BLM land means and why it's such a significant topic in discussions about public land use and conservation? BLM land, managed by the Bureau of Land Management, plays a crucial role in preserving natural resources, supporting recreational activities, and maintaining ecological balance. Understanding its meaning and importance is essential for anyone interested in environmental sustainability and responsible land use. Whether you're an outdoor enthusiast, a conservation advocate, or simply curious, this article will provide a detailed explanation of BLM land, its purpose, and its impact on both the environment and local communities.
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is a federal agency under the U.S. Department of the Interior. It oversees millions of acres of public land across the United States, primarily in the western states. These lands are designated for multiple uses, including recreation, grazing, energy development, and conservation. BLM land serves as a vital resource for the nation, balancing economic, environmental, and cultural priorities. This article will explore the history, management practices, and significance of BLM land, offering insights into how it affects our lives and the natural world.
As you read further, you'll discover the intricacies of BLM land management, its role in preserving biodiversity, and its contribution to outdoor recreation. You'll also learn about the challenges and controversies surrounding these lands, as well as how individuals can engage responsibly with them. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of what BLM land means and why it matters for both current and future generations.
Read also:Unveiling The Role Of Mike Majlaks Assistant A Behindthescenes Look
Table of Contents
What is BLM Land?
BLM land refers to the vast tracts of public land managed by the Bureau of Land Management. These lands cover approximately 245 million acres, primarily located in the western United States, including states like Nevada, Alaska, Utah, and Wyoming. The primary mission of the BLM is to sustain the health, diversity, and productivity of these lands for the use and enjoyment of present and future generations. This includes balancing multiple uses such as recreation, livestock grazing, mineral extraction, and conservation.
Types of BLM Land
BLM land is not a single, uniform category but rather encompasses various types of landscapes and ecosystems. These include:
- Deserts: Arid regions that support unique flora and fauna adapted to dry conditions.
- Forests: Wooded areas that provide habitat for wildlife and resources for timber production.
- Grasslands: Open plains used for grazing and maintaining biodiversity.
- Rivers and Wetlands: Vital water sources that support aquatic ecosystems and human communities.
Key Features of BLM Land
One of the defining features of BLM land is its accessibility to the public. Unlike private or state-owned lands, BLM land is open for a wide range of activities, including hiking, camping, hunting, fishing, and off-road vehicle use. However, these activities are subject to regulations designed to protect the land's natural and cultural resources. Additionally, BLM land often contains significant cultural and historical sites, such as ancient Native American ruins and pioneer trails.
History of BLM Land
The history of BLM land dates back to the early days of the United States, when vast tracts of land were acquired through treaties, purchases, and conquests. Initially, these lands were seen as a resource to be exploited for economic gain, but over time, the federal government recognized the need for sustainable management practices.
Formation of the Bureau of Land Management
The Bureau of Land Management was established in 1946 through the merger of two agencies: the General Land Office and the Grazing Service. This consolidation aimed to streamline the management of public lands and address growing concerns about overgrazing, soil erosion, and resource depletion. Since its inception, the BLM has evolved to focus on multiple-use and sustained-yield principles, ensuring that public lands benefit a wide range of stakeholders.
Key Milestones in BLM History
- 1964: Passage of the Wilderness Act, which designated certain BLM lands as protected wilderness areas.
- 1976: Enactment of the Federal Land Policy and Management Act (FLPMA), which established a framework for managing BLM lands.
- 1990s: Increased emphasis on conservation and environmental protection, including habitat restoration and endangered species management.
Management and Regulations
Managing BLM land involves balancing competing interests and ensuring that these lands are used sustainably. The BLM employs a variety of tools and strategies to achieve this goal, including land-use planning, environmental assessments, and partnerships with local communities and stakeholders.
Read also:Unraveling The Mystery Of Storage Wars Death 2024
Land-Use Planning
Land-use planning is a cornerstone of BLM management. Through this process, the agency develops comprehensive plans that outline how specific areas of BLM land will be used and protected. These plans consider factors such as ecological sensitivity, cultural significance, and economic potential. Public input is a critical component of land-use planning, ensuring that diverse perspectives are considered.
Regulations and Enforcement
The BLM enforces a range of regulations to protect the natural and cultural resources of its lands. These regulations cover activities such as mining, grazing, and recreational use. Violations can result in fines, permit revocations, or legal action. The agency also collaborates with other federal, state, and local entities to monitor and enforce compliance.
Recreational Opportunities on BLM Land
BLM land offers a wealth of recreational opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts. From hiking and camping to hunting and off-roading, these lands provide a diverse range of activities for people of all ages and interests.
Popular Activities
- Hiking and Backpacking: BLM land features numerous trails that cater to hikers of all skill levels.
- Camping: Dispersed camping is allowed in many areas, offering a chance to experience remote wilderness.
- Hunting and Fishing: BLM lands are home to diverse wildlife populations, making them popular destinations for hunters and anglers.
- Off-Roading: Designated areas allow for off-road vehicle use, including ATVs and dirt bikes.
Responsible Recreation
While BLM land is open for recreation, it's essential to follow Leave No Trace principles to minimize your impact. This includes packing out trash, staying on designated trails, and respecting wildlife and cultural sites. By practicing responsible recreation, visitors can help preserve these lands for future generations.
Environmental Conservation Efforts
Conservation is a key priority for the BLM, as these lands are home to a wide variety of ecosystems and species. The agency works to protect habitats, restore degraded areas, and manage resources sustainably.
Habitat Protection
BLM land provides critical habitat for numerous plant and animal species, including many that are endangered or threatened. The agency implements measures to protect these species, such as restricting certain activities in sensitive areas and restoring degraded habitats.
Restoration Projects
The BLM undertakes various restoration projects to improve the health and resilience of its lands. These projects may involve reseeding native plants, removing invasive species, or rehabilitating areas affected by wildfires or mining activities.
Economic Impact of BLM Land
BLM land contributes significantly to the U.S. economy by supporting industries such as agriculture, energy, and tourism. These lands provide resources and opportunities that generate jobs and revenue for local communities.
Energy Development
BLM land is a major source of energy resources, including oil, gas, coal, and renewable energy. The agency leases land for energy development, subject to environmental and safety regulations. This activity supports energy independence and economic growth.
Tourism and Recreation
Recreational activities on BLM land attract millions of visitors each year, contributing to local economies through spending on lodging, food, and equipment. This tourism also raises awareness about the importance of public lands and conservation.
Controversies and Challenges
Despite its many benefits, BLM land management is not without controversy. Conflicts often arise over competing uses, such as grazing versus conservation or energy development versus environmental protection.
Grazing Conflicts
Grazing on BLM land has been a longstanding issue, with debates over the environmental impact of livestock and the rights of ranchers. The agency works to balance these interests through grazing permits and land-use planning.
Environmental Concerns
Energy development and other activities on BLM land can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. The agency addresses these concerns through environmental assessments and mitigation measures.
How to Engage Responsibly with BLM Land
Engaging responsibly with BLM land is crucial for preserving its natural and cultural resources. Whether you're a visitor, a landowner, or a stakeholder, there are steps you can take to support sustainable land use.
Leave No Trace Principles
Adhering to Leave No Trace principles is one of the most effective ways to minimize your impact on BLM land. This includes packing out all trash, avoiding sensitive areas, and respecting wildlife.
Volunteer and Advocate
You can also get involved by volunteering for conservation projects or advocating for policies that protect public lands. Many organizations partner with the BLM to support its mission and engage the public.
Success Stories: BLM Land in Action
There are numerous success stories that highlight the positive impact of BLM land management. These stories demonstrate how collaboration, innovation, and dedication can lead to meaningful outcomes.
Wildlife Conservation
One notable success is the recovery of the sage-grouse, a bird species that depends on BLM-managed habitats. Through habitat restoration and conservation efforts, populations have stabilized in many areas.
Community Partnerships
Partnerships with local communities have also led to successful projects, such as trail development and cultural preservation. These collaborations strengthen the connection between people and public lands.
Conclusion
BLM land is a vital resource that supports recreation, conservation, and economic development. By understanding its meaning and significance, we can better appreciate the role these lands play in our lives and the environment. Whether you're an outdoor enthusiast, a conservation advocate, or simply curious, there are many ways to engage with and support BLM land.
We encourage you to explore these lands responsibly, advocate for their protection, and share your experiences with others. Together, we can ensure that BLM land continues to benefit both people and nature for generations to come. If you found this article helpful, consider leaving a comment, sharing it with friends, or reading more about public lands and conservation efforts on our site.